An Introduction to ASP.NET Web API
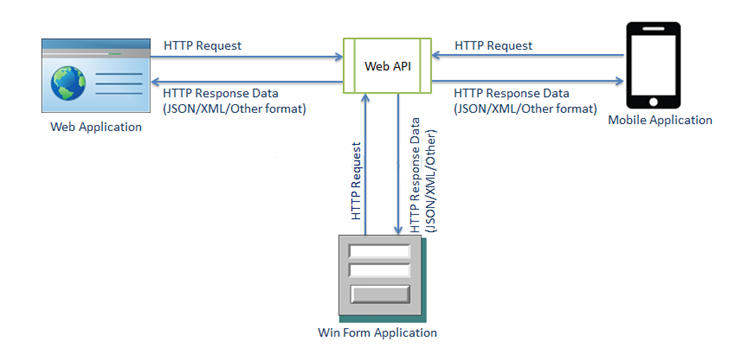
ASP.NET Web API is a framework which is used for building HTTP based services which can be accessed on different platforms such as web, windows, mobile etc.
How does it Work?
It works nearly the same way as ASP.NET MVC web application. Difference is that Web API sends data as a response while MVC application sends html view. Web API is like a web service or WCF service but it only supports HTTP protocol.
ASP.NET Web API Characteristics
- It is an ideal platform for building RESTFul services.
- It is built on top of ASP.NET and supports ASP.NET request/response pipeline.
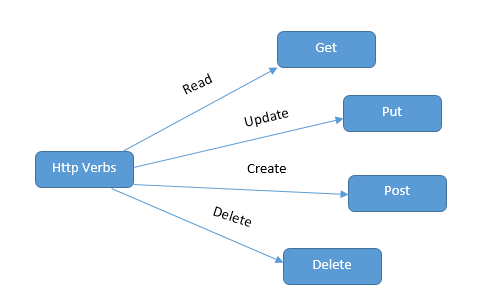
- It maps HTTP verbs like Get, Put, Post and Delete to method names.
- It supports different formats of response data and has built-in support for JSON, XML, and BSON format.
- It can be hosted in IIS, Self-hosted or other web server that supports .NET 4.0+.
- Web API framework includes HttpClient to communicate with Web API server. HttpClient can be used in ASP.MVC server side, Windows Form application, Console application or other apps.
Authentication and Authorization in ASP.NET Web API
Authentication is used to know the identity of the user. For example, any user logs in with username and password, and the server uses the password to authenticate user.
Authorization will come after authentication. In authentication we need to decide whether a user is allowed to perform an action or not. For example, User has permission to get a resource but not create a resource.
Versioning in ASP.NET Web API
Versioning helps us to provide specific information to specific user. Now a days multiple users are consuming Web API at a time so whenever the business requirement gets changed we need to update the Web API which will work for specific user without affecting the existing users. In order to hand such situations we need Versioning.
1. URI based Versioning
In this method, with help of routing Web API URI gets changed and make it more readable. Example: we have an existing running API which is returning same response for all clients. Now if any one client wants some changes by requesting some parameters then with versioning we can achieve it without breaking any existing API.
2. Query String based Versioning
In this method a query string parameter is added to the query string in order to find the controller or Action to which request is sent. So different parameters will find different action or controller which helps in versioning.
3. Custom Header parameter based Versioning
Custom Headers are used for troubleshooting, providing additional information and implementing server-side logic, etc. Version information can be send in the custom header and check its value and return the response according to its value.
4. Accept Header parameter based Versioning
Accepts Headers requests the server and asks for the file format of the data which is required by the browser. Data is defined as MIME Types which stands for “Multipurpose Internet Mail Exchange”. MIME type is generally case-insensitive, but it is generally written in small letters.
Learn more – Authentication and Authorization in ASP.NET Web API
Advantages of WEB API over WCF
- Now a days in this fast growing technology environment it is difficult to decide whether to use WEB API or WCF (Windows Communication Foundation). Both are self-hosted or can be hosted in IIS.
- In the scenarios like end-to-end message security, distributed transactions, message queues, duplex communication, one way messaging, etc. use of WCF is best.
- WEB API is more suitable when we are working with MVC-based applications. It is also used for creating a resource-oriented services using HTTP/Restful.
- WCF was created to generally develop SOAP-based services and bindings. As it is SOAP based, it is using standard XML schema over HTTP, which results into slower performance.
- On other side, WEB API is a good choice for simpler, light weight services. WEB API can use any text format including XML and is faster than WCF. Also it doesn’t require any data contracts and doesn’t require configurations in comparison with WCF.
- If our criteria is performance and quick development then WEB API is a better choice over WCF.
Author – Sahil Joshi














Get in Touch